Catalyzing Nanotechnology
Catalyzing Nanotechnology by David Pescovitz, ScienceMatters@Berkeley.
The researchers have also explored a method to imprint bulk silica with particle templates as large as 15 nanometers. Rather than organize several functional groups at a time, the synthesis of nanoparticle building blocks for bulk silica imprinting is ideal for organizing thousands of functional groups at once, Katz says.
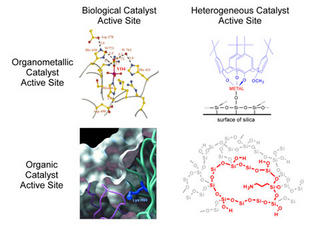
This slide depicts the synthetic and biological catalysts consisting of similar organic and organometallic active sites. The confined environment surrounding both biological catalysts results from the hydrophobic interior of the enzyme. The researchers successfully replicated this confinement in the synthetic equivalents of the biological active sites shown on the right side of this figure. (courtesy the researchers)
This slide depicts the synthetic and biological catalysts consisting of similar organic and organometallic active sites. The confined environment surrounding both biological catalysts results from the hydrophobic interior of the enzyme. The researchers successfully replicated this confinement in the synthetic equivalents of the biological active sites shown on the right side of this figure. (courtesy the researchers)
Friday, October 21, 2005 1:54 PM ::  ::
::
Post a Comment
permalink to Catalyzing Nanotechnology
0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home
permalink to Catalyzing Nanotechnology


